DBMS Benchmarker Python Package


DBMS-Benchmarker
DBMS-Benchmarker is a Python-based application-level blackbox benchmark tool for Database Management Systems (DBMS). It aims at reproducible measuring and easy evaluation of the performance the user receives even in complex benchmark situations. It connects to a given list of DBMS (via JDBC) and runs a given list of (SQL) benchmark queries. Queries can be parametrized and randomized. Results and evaluations are available via a Python interface and can be inspected with standard Python tools like pandas DataFrames. An interactive visual dashboard assists in multi-dimensional analysis of the results.
See the homepage and the documentation.
If you encounter any issues, please report them to our Github issue tracker.
Key Features
DBMS-Benchmarker
is Python3-based
helps to benchmark DBMS
connects to all DBMS having a JDBC interface - including GPU-enhanced DBMS
requires only JDBC - no vendor specific supplements are used
benchmarks arbitrary SQL queries - in all dialects
allows planning of complex test scenarios - to simulate realistic or revealing use cases
allows easy repetition of benchmarks in varying settings - different hardware, DBMS, DBMS configurations, DB settings etc
investigates a number of timing aspects - connection, execution, data transfer, in total, per session etc
investigates a number of other aspects - received result sets, precision, number of clients
collects hardware metrics from a Prometheus server - hardware utilization, energy consumption etc
helps to evaluate results - by providing
metrics that can be analyzed by aggregation in multi-dimensions, like maximum throughput per DBMS, average CPU utilization per query or geometric mean of run latency per workload
predefined evaluations like statistics
in standard Python data structures
see rendered example
in an interactive dashboard
For more informations, see a basic example or take a look in the documentation for a full list of options.
The code uses several Python modules, in particular jaydebeapi for handling DBMS. This module has been tested with Citus Data (Hyperscale), Clickhouse, CockroachDB, Exasol, IBM DB2, MariaDB, MariaDB Columnstore, MemSQL (SingleStore), MonetDB, MySQL, OmniSci (HEAVY.AI), Oracle DB, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, SAP HANA, TimescaleDB, and Vertica.
Installation
Run pip install dbmsbenchmarker to install the package.
You will also need to have
Java [installed](https://www.java.com/en/download/help/download_options.html) (we tested with Java 8)
JAVA_HOMEset correctlya JDBC driver suitable for the DBMS you want to connect to (optionally located in your
CLASSPATH)
Basic Usage
The following very simple use case runs the query SELECT COUNT(*) FROM test 10 times against one local MySQL installation.
As a result we obtain an interactive dashboard to inspect timing aspects.
Configuration
We need to provide
a [DBMS configuration file](https://dbmsbenchmarker.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Options.html#connection-file), e.g. in
./config/connections.config
[
{
'name': "MySQL",
'active': True,
'JDBC': {
'driver': "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver",
'url': "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/database",
'auth': ["username", "password"],
'jar': "mysql-connector-java-8.0.13.jar"
}
}
]
the required JDBC driver, e.g.
mysql-connector-java-8.0.13.jara [Queries configuration file](https://dbmsbenchmarker.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Options.html#query-file), e.g. in
./config/queries.config
{
'name': 'Some simple queries',
'connectionmanagement': {
'timeout': 5 # in seconds
},
'queries':
[
{
'title': "Count all rows in test",
'query': "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM test",
'numRun': 10
}
]
}
Perform Benchmark
Run the CLI command: dbmsbenchmarker run -e yes -b -f ./config
-e yes: This will precompile some evaluations and generate the timer cube.-b: This will suppress some output-f: This points to a folder having the configuration files.
This is equivalent to python benchmark.py run -e yes -b -f ./config
After benchmarking has been finished we will see a message like
Experiment <code> has been finished
The script has created a result folder in the current directory containing the results. <code> is the name of the folder.
Evaluate Results in Dashboard
Run the command: dbmsdashboard
This will start the evaluation dashboard at localhost:8050.
Visit the address in a browser and select the experiment <code>.
Alternatively you may use a [Jupyter notebook](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/DBMS-Benchmarker/blob/master/Evaluation-Demo.ipynb), see a [rendered example](https://beuth-erdelt.github.io/DBMS-Benchmarker/Evaluation-Demo.html).
Limitations
Limitations are:
strict black box perspective - may not use all tricks available for a DBMS
strict JDBC perspective - depends on a JVM and provided drivers
strict user perspective - client system, network connection and other host workloads may affect performance
not officially applicable for well known benchmark standards - partially, but not fully complying with TPC-H and TPC-DS
hardware metrics are collected from a monitoring system - not as precise as profiling
no GUI for configuration
strictly Python - a very good and widely used language, but maybe not your choice
Other comparable products you might like
[Apache JMeter](https://jmeter.apache.org/index.html) - Java-based performance measure tool, including a configuration GUI and reporting to HTML
[HammerDB](https://www.hammerdb.com/) - industry accepted benchmark tool based on Tcl, but limited to some DBMS
[Sysbench](https://github.com/akopytov/sysbench) - a scriptable multi-threaded benchmark tool based on LuaJIT
[OLTPBench](https://github.com/oltpbenchmark/oltpbench) - Java-based performance measure tool, using JDBC and including a lot of predefined benchmarks
[BenchBase](https://github.com/cmu-db/benchbase) - successor of OLTPBench
Contributing, Bug Reports
If you have any question or found a bug, please report them to our [Github issue tracker](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/DBMS-Benchmarker/issues). In any bug report, please let us know:
Which operating system and hardware (32 bit or 64 bit) you are using
Python version
DBMSBenchmarker version (or git commit/date)
DBMS you are connecting to
Traceback that occurs (the full error message)
We are always looking for people interested in helping with code development, documentation writing, technical administration, and whatever else comes up. If you wish to contribute, please first read the [contribution section](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/DBMS-Benchmarker/blob/master/docs/CONTRIBUTING.md) or visit the [documentation](https://dbmsbenchmarker.readthedocs.io/en/latest/CONTRIBUTING.html).
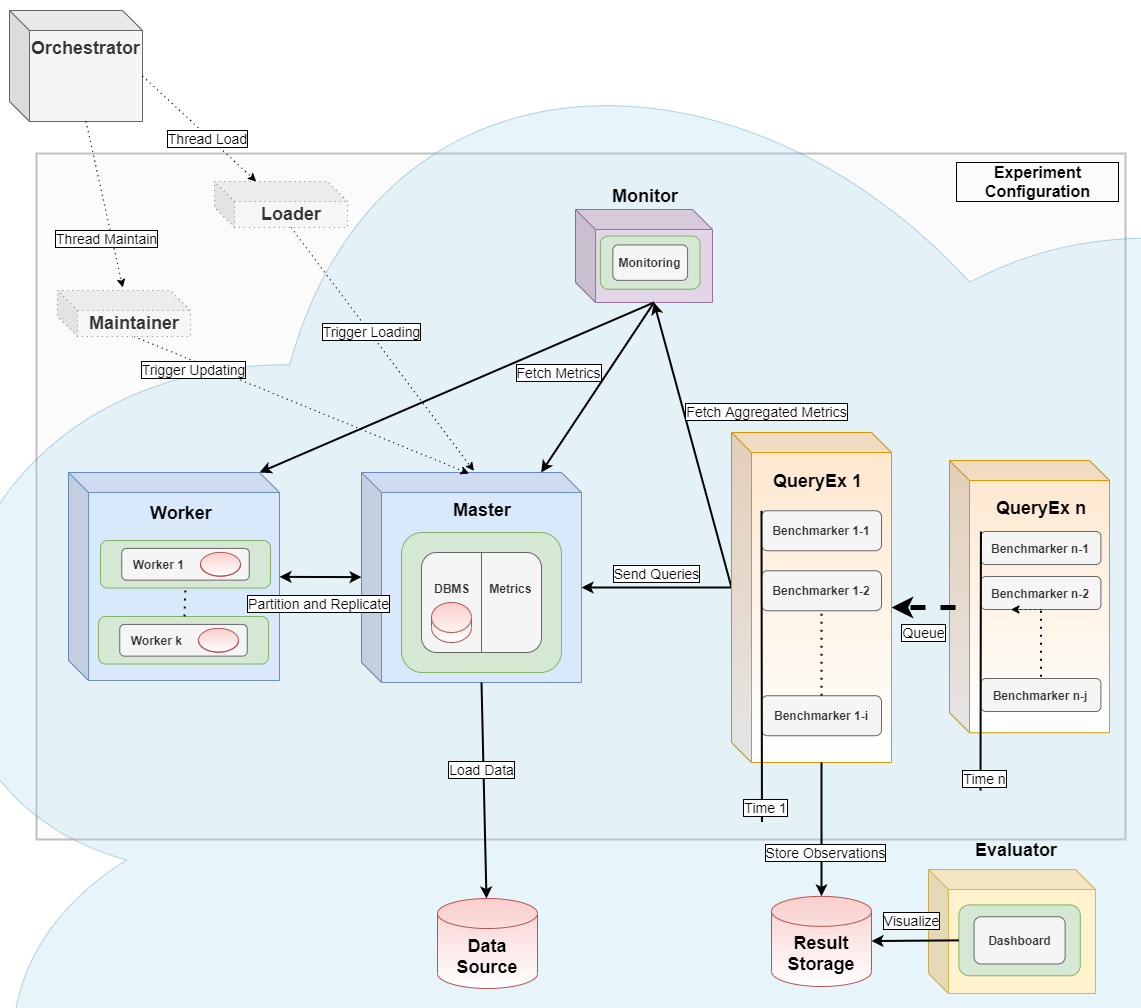
Benchmarking in a Kubernetes Cloud
This module can serve as the query executor [2] and evaluator [1] for distributed parallel benchmarking experiments in a Kubernetes Cloud, see the [orchestrator](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager) for more details.
References
If you use DBMSBenchmarker in work contributing to a scientific publication, we kindly ask that you cite our application note [1] and/or [3]:
[1] [A Framework for Supporting Repetition and Evaluation in the Process of Cloud-Based DBMS Performance Benchmarking](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84924-5_6)
Erdelt P.K. (2021) A Framework for Supporting Repetition and Evaluation in the Process of Cloud-Based DBMS Performance Benchmarking. In: Nambiar R., Poess M. (eds) Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking. TPCTC 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12752. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84924-5_6
[2] [Orchestrating DBMS Benchmarking in the Cloud with Kubernetes](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94437-7_6)
Erdelt P.K. (2022) Orchestrating DBMS Benchmarking in the Cloud with Kubernetes. In: Nambiar R., Poess M. (eds) Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking. TPCTC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13169. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94437-7_6
[3] [DBMS-Benchmarker: Benchmark and Evaluate DBMS in Python](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.04628)
Erdelt P.K., Jestel J. (2022). DBMS-Benchmarker: Benchmark and Evaluate DBMS in Python. Journal of Open Source Software, 7(79), 4628 https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.04628